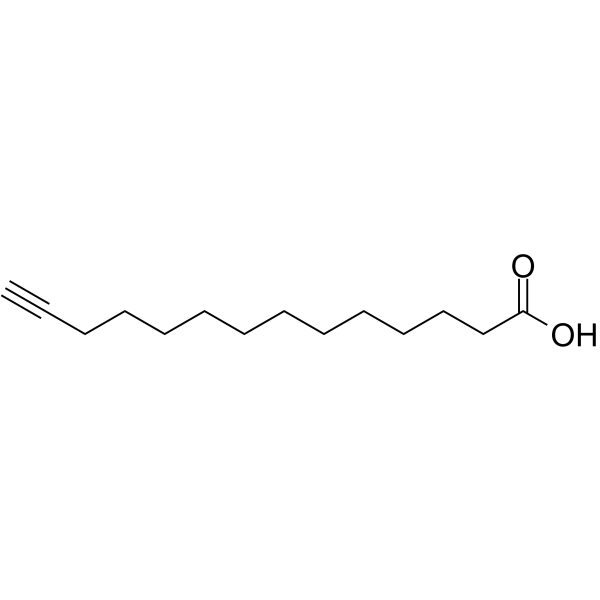
Alkynyl myristic acid
CAS No. 82909-47-5
Alkynyl myristic acid( 13-Tetradecynoic acid | tetradec-13-ynoic acid | 13-Tetradecyn-1-oic acid )
Catalog No. M26602 CAS No. 82909-47-5
Alkynyl myristic acid is an alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 46 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 69 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 143 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 237 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 357 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 842 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAlkynyl myristic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAlkynyl myristic acid is an alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
DescriptionAlkynyl myristic acid is an alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.(In Vitro):PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.
-
In VitroPROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms13-Tetradecynoic acid | tetradec-13-ynoic acid | 13-Tetradecyn-1-oic acid
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorAntifungal
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number82909-47-5
-
Formula Weight224.344
-
Molecular FormulaC14H24O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (445.75 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCC#C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.I Kubo, et al. Polygodial, an antifungal potentiator. J Nat Prod. Jan-Feb 1988;51(1):22-9.
molnova catalog



related products
-
DuP 105
DuP 105 is an orally active oxazolidinone, a new class of synthetic antimicrobial agent with activity against gram-positive bacteria.
-
SGC-CBP30
SGC-CBP30 is an effective CREBBP/EP300 inhibitor (IC50: 21/38 nM).
-
Epidermal Mitosis In...
Epidermal Mitosis Inhibiting Pentapeptide



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


